Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injuries are common among athletes and active individuals, particularly those involved in sports requiring sudden changes in direction or intense physical activity. The ACL is a critical ligament in the knee that provides stability and helps control movement.
Causes of ACL Injuries
ACL injuries often occur during activities that involve jumping, rapid direction changes, or direct impacts to the knee. Common scenarios include sports like soccer, basketball, and skiing. The injury typically happens when the ligament is overstretched or torn due to excessive force or sudden movements.
Symptoms of an ACL Injury
Symptoms of an ACL injury can vary in severity but often include:
- A loud “pop” or tearing sensation at the time of injury
- Severe pain and swelling
- Limited range of motion
- Instability or the feeling that the knee might give out
Diagnosis
Diagnosis usually involves a physical examination and imaging tests such as MRI or X-rays to confirm the extent of the injury. An orthopedic specialist will assess the injury and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options
Treatment for ACL injuries can be non-surgical or surgical, depending on the severity of the tear and the patient’s activity level.
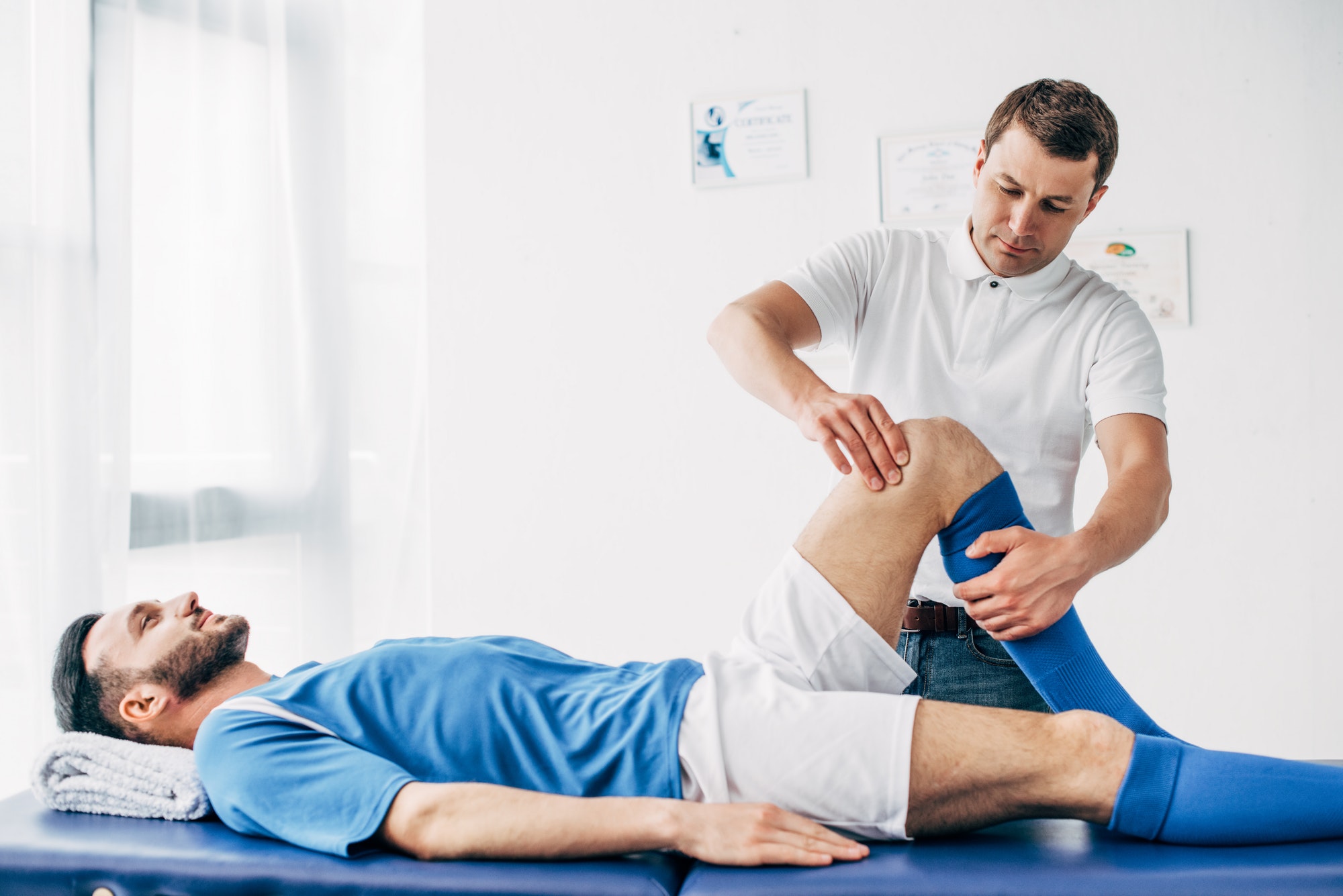
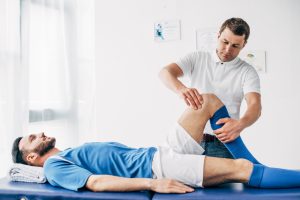
- Non-Surgical Treatment: This approach is suitable for partial tears or less active individuals. It typically includes physical therapy, bracing, and rest to manage pain and improve knee function.
- Surgical Treatment: For complete tears or athletes who wish to return to high-level activities, surgery is often recommended. ACL reconstruction involves replacing the torn ligament with a graft, usually taken from the patient’s own body or a donor. Rehabilitation following surgery is crucial and involves physical therapy to restore strength and flexibility.
Prevention
Preventing ACL injuries involves proper training and conditioning:
- Strength Training: Strengthening the muscles around the knee can provide additional support and reduce the risk of injury.
- Proper Technique: Learning and using correct techniques for jumping and landing can minimize stress on the ACL.
- Flexibility and Balance: Incorporating exercises that improve flexibility and balance can also help prevent injuries.